200以上 (f g)(x) 219009-F(g(x)) solver
A) The function f(g(x)) is the derivative of g in terms of x B) The function f(g(x)) is the product of f(x) and g(x) C) The function f(g(x)) is the result of substituting x in place of the independent variable in the expression for f D) the composition of functions f(g(x)) is the result if substituting g, expressed in terms of the independentF (g(x)) f ( g ( x)) Evaluate f (g(x)) f ( g ( x)) by substituting in the value of g g into f f f (x2) = 3(x2)−4 f ( x 2) = 3 ( x 2) 4 Simplify each term Tap for more steps Apply the distributive property f ( x 2) = 3 x 3 ⋅ 2 − 4 f ( x 2) = 3 x 3 ⋅ 2 4 Multiply 3 3 by 2 2 f ( x 2) = 3 x 6 − 4 f ( x 2Added Aug 1, 10 by ihsankhairir in Mathematics To obtain the composite function fg(x) from known functions f(x) and g(x) Use the hatch symbol # as the variable when inputting

Adidas X Ghosted 3 Laceless Fg Fw3541 Www Daka Nl
F(g(x)) solver
F(g(x)) solver-Power Rule (d/dx) (x n ) = nx n1;Given f (x) = 2x, g(x) = x 4, and h(x) = 5 – x 3, find (f g)(2), (h – g)(2), (f × h)(2), and (h / g)(2) This exercise differs from the previous one in that I not only have to do the operations with the functions, but I also have to evaluate at a particular x value




Adidas Heren Voetbalschoenen Fg X Ghosted 3 Fg Eh23 Kopen Bij Voorwinden Nl
Operaciones en funciones Las funciones con dominios que se traslapan pueden ser sumadas, restadas, multiplicadas y divididas Si f ( x ) y g ( x ) son dos funciones, entonces para todas las x en el dominio de ambas funciones la suma, diferencia, producto y cociente están definidos como sigue ( f g ) ( x ) = f ( x ) g ( x )(fg)(x) o = f(g(x)), notice that in the case the function g is inside of the function f In composite functions it is very important that we pay close attention to the order in which the compositionAnd "( f o g)(x)" means "f (g(x))" That is, you plug something in for x, then you plug that value into g, simplify, and then plug the result into f The process here is just like what we saw on the previous page, except that now we will be using formulas to find values, rather than just reading the values from lists of points Given f(x) = 2x
Learn how to solve f(g(x)) by replacing the x found in the outside function f(x) by g(x)Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutorAn online gof fog calculator to find the (fog) (x) and (gof) (x) for the given functions In this online fog x and gof x calculator enter the f (x) and g (x) and submit to know the fog gof function Code to add this calci to your website Just copy and paste the below code to your webpage where you want to display this calculator
The domain of the (f ·g)(x) consists of all xvalues that are in the domain of both f and g In this example, f has domain {x x ≠ 0}, and g has domain all real numbers, therefore (f · g)(x) has domain {x x ≠ 0}, because these values of x are in the domain of both f and gProof of f(x) g(x) = f(x) g(x) from the definition We can use the definition of the derivativeCalculates a table of the given functions f(x) and g(x) and draws the chart f(x) g(x) range (a, b) partitions n Customer Voice Questionnaire FAQ Chart drawing f(x),g(x) 15 /5 DispNum 1 0454 / 60 years old level or over / A teacher / A researcher / Useful /




Function Arithmetic Finding F G X F G X Fg X And F G X Youtube



Adidas Inflight X Ghosted 2 Fg Heren Jd Sports
Derivative of a constant multiplied with function f (d/dx) (a f) = af' Sum Rule (d/dx) (f ± g) = fSolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreF(g(x)) is read as "f of g of x" f(g(x)) can also be written as (f ∘ g)(x) or fg(x), In the composition (f ∘ g)(x), the domain of f becomes g(x) The following diagram shows some examples of composite functions Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions




Adidas X 19 3 Gras Voetbalschoenen Fg Zwart Zwart




Adidas X Ghosted 3 Laceless Fg Fw3541 Www Daka Nl
So now G of f of X be equal to G off four X plus four, which is equal to 025 4 That's plus four minus one This is then equal two We multiply this out one X plus one minus one, which is equal to X and again there is no restriction on what values X could take So this is true for all the values in the domain of FFirst write the composition in any form like \( (go f) (x) as g (f(x)) or (g o f) (x^2) as g (f(x^2))\) Put the value of x in the outer function with the inside function then just simplify the function Although, you can manually determine composite functions byFind (fg)(x), (fg)(x), (f*g)(x) and (f/g)(x) for each f(x) and g(x) 2 f(x)= 8x^2 g(x)=1/x^2 I'm having trouble understanding what i have to do, please help This question is from textbook Algebra2 Answer by jim_thompson5910() (Show Source)



Use The Quotient Rule F G F G Fg G 2 To Find The Derivative Of F X G X



Groen Adidas Precision To Blur X Ghosted 1 Fg Kinderen Jd Sports
Both f and g are the functions of x and differentiated with respect to x We can also represent dy/dx = D x y Some of the general differentiation formulas are;Mar 07, 21 · Transcribed image text Find f g, fg, fg, and f/g and their domains f(x) = x, g(x) = 7x Find (f g)(x) Find the domain of (f g)(x) (Enter your answer using interval notation) Find (f g)(x) Find the domain of (f g)(x) (Enter your answer using interval notation) Find (fg)(x) Find the domain of (fg)(x)Proof of f(g(x)) = f(g) * g(x) from the definition We can use the definition of the derivative




Adidas X Ghosted 1 Fg Marvel X Men Pro Keepers Line
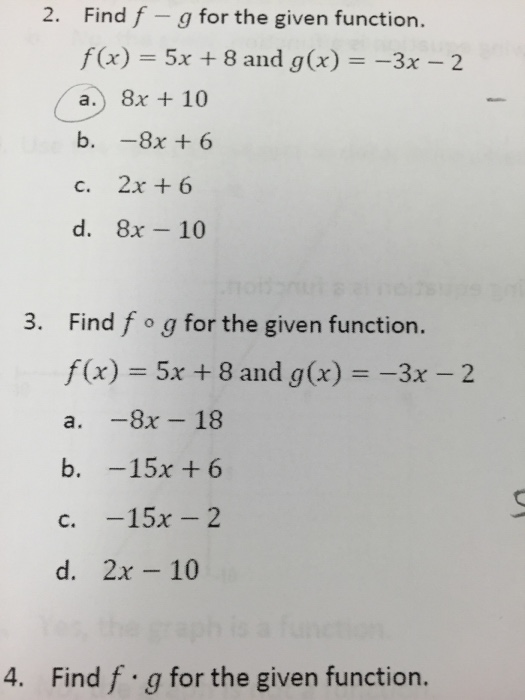



Find F G For The Given Function F X 5x 8 And Chegg Com
F of X is equal to 7x minus 5 G of X is equal to X to the third power plus 4x and then they asked us to find F times G of X so the first thing to realize that this notation F times G of X it's just referring to a function that is a product of f of X and G of X so by definition this notation just means f of X f of X x times G of X and then we just have to substitute f of X with this definitionCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyDerivative of a constant, a (d/dx) (a) = 0;
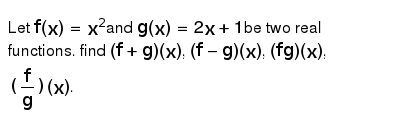



Let F X X 2and G X 2x 1be Two Real Functions Find




Answered The Functions F And G Are Defined As Bartleby
For example, if f is a function that has the real numbers as domain and codomain, then a function mapping the value x to the value g(x) = 1 / f(x) is a function g from the reals to the reals, whose domain is the set of the reals x, such that f(x) ≠ 0 The range of a function is the set of the images of all elements in the domainPost your questions to our community of 350 million students and teachers Get expert, verified answers Learn faster and improve your gradesDec 16, 14 · It's f^prime(g(h(x))) g^prime (h(x)) h^prime(x) Start by defining the function a(x)=g(h(x)) The the chain rule gives us (f @ g @ h)^prime (x)=(f @ alpha)^prime (x)=f^prime(alpha(x)) alpha^prime(x) Applying the definition of alpha(x) to the equation above gives us f^prime(alpha(x)) alpha^prime(x) = f^prime (g(h(x))) (g @h)^prime (x) Using the chain rule again f^prime (g(h(x))) (g



Adidas X Ghosted 2 Fg Voetbalschoenen Zwart
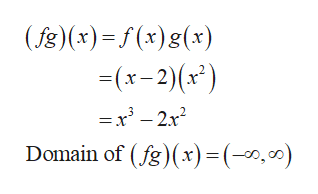



Answered Consider The Following Functions F X Bartleby
Since (f/g)(x) = f(x)/g(x) for x to be in the domain of (f/g)(x) it must be in the domain of f and in the domain of g You also need to insure that g(x) is not zero since f(x) is divided by g(x) Thus there are 3 conditions x must be in the domain of f f(x) = 3x 5 and all real numbers x are in the domain of xAssuming that these functions are actually vectors in a function space, you just use the definition of addition of vectors To be precise, we can imagine a function as a vector with infinite (continuous) values;Lets open up the function grapher and explore with some specific f(x), g(x), and the resulting h(x) Lets try The graphs on the same set of axes are For some novices, seeing the graph of the product h(x) = (3x 2)(2x1) and the graphs of the two straight lines from the factors on the same coordinate axes provides a new experience This




Warm Up Arithmetic Combinations F G X F X G X F G X F X G X Fg X F X G X F G X F X G X 0 G X The Domain For These Ppt Download




Ford Falcon Fg X Wikipedia
The inside function is performed first, and the outside function is performed second So if f (g (x))= (5x^22)^2, then one possibility could be g (x)=5x^22 for the inside function, and f (x)=x^2 for the outside function (By the way, this is not the only possibilityThe Algebra of Functions Like terms, functions may be combined by addition, subtraction, multiplication or division Example 1 Given f ( x ) = 2x 1 and g ( x ) = x2 2x – 1 find ( f g ) ( x ) and ( f g ) ( 2 )1 Introduction The composition of two functions g and f is the new function we get by performing f first, and then performing g For example, if we let f be the function given by f(x) = x2 and let g be the function given by g(x) = x3, then the composition of g with f is called gf and is worked out
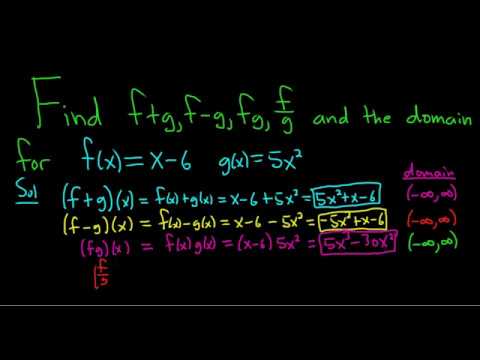



How To Find F G F G Fg And F G And The Domain Of Each Youtube
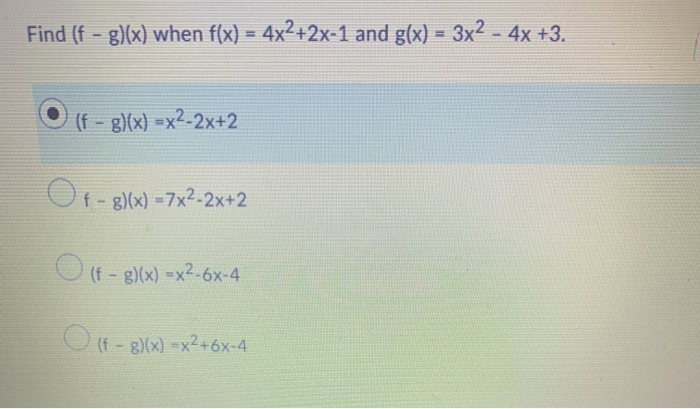



Find F G X When F X 4x2 2x 1 And G X 3x2 Chegg Com
Answer to Find (fg)(x), (f g)(x), (fg)(x), and (f/g)(x) and their domains f(x) = x,\\ g(x) = 9x By signing up, you'll get thousands ofIn this video we learn about function composition Composite functions are combinations of more than one function In this video we learn about f(g(x)) and gIf f(x) and g(x) are differentiable functions, then the derivative of the product fg with respect to x is given by (fg)' = f 'g f g' This can be fairly easily derived from the definition Example To calculate the derivative of h(x) = x 2 e x we must use the product rule The Quotient Rule If f(x) and g(x) are differentiable functions and g



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Ap16 Calculus Ab Q6 Pdf



Composite Functions
F(x)=2x3,\g(x)=x^25,\(f\circ \g)(2) functioncompositioncalculator en Related Symbolab blog posts Intermediate Math Solutions – Functions Calculator, Function Composition Function composition is when you apply one function to the results of another function When referring toIn mathematics, function composition is an operation that takes two functions f and g and produces a function h such that h(x) = g(f(x))In this operation, the function g is applied to the result of applying the function f to xThat is, the functions f X → Y and g Y → Z are composed to yield a function that maps x in X to g(f(x)) in Z Intuitively, if z is a function of y, and y is aComposite functions and Evaluating functions f(x), g(x), fog(x), gof(x) Calculator 1 f(x)=2x1, g(x)=x5, Find fog(x) 2 fog(x)=(x2)/(3x), f(x)=x2, Find gof(x




Which Functions Defines F G X Brainly Com
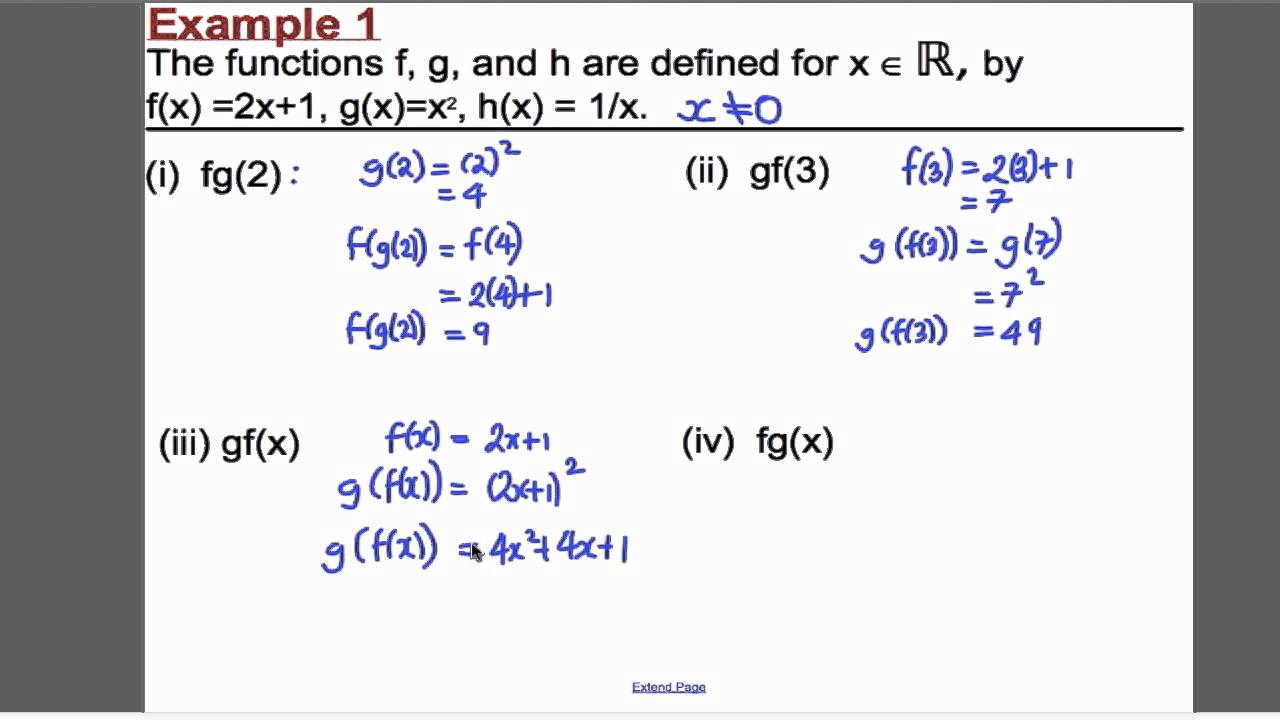



Composite Function Exam Questions Examples Solutions Worksheets Videos Activities
G(x) = f (x k), can be sketched by shifting f (x) k units horizontally Vertical Stretches and Shrinks For the base function f (x) and a constant k > 0, the function given by g(x) = k f (x), can be sketched by vertically stretching f (x) by a factor of k if k > 1 orIt follows that f (f (x)) = g (x) for all x outside I There are 2 R many such h's, and hence also this many f'sQED If g is continuous, then this f can be chosen also to be continuous By using a Cantor set instead of an interval, one can find a function f that solves f (f (x)) = g (x) except on aJan 25, 17 · A function f (x) and g (x) then (f g) (x) = x² x 6 Further explanation Like the number operations we do in real numbers, operations such as addition, installation, division or multiplication can also be done on two functions




Let F And G Be Real Functions Defined By F X Sqrt X 2 Andg X S




2 6 Combining Functions Flashcards Quizlet
Determine composite and inverse functions for trigonometric, logarithmic, exponential or algebraic functions as part of Bitesize Higher MathsThe Chain Rule says the derivative of f (g (x)) = f' (g (x))g' (x) The individual derivatives are f' (g) = cos (g) g' (x) = 2x So d dx sin (x 2) = cos (g (x)) (2x) = 2x cos (x 2) Another way of writing the Chain Rule is dy dx = dy du du dxInstead of speaking about the value




Adidas X Ghosted 3 Laceless Fg Fw3541 Www Daka Nl



Adidas X Ghosted 3 Fg Voetbalschoenen Zwart
Fxgx=x\sqrt {x1} f x g x = x x − 1 Subtract gx from both sides Subtract g x from both sides fx=x\sqrt {x1}gx f x = x x − 1 − g x The equation is in standard form The equation is in standard form xf=gxx\sqrt {x1}Apr 29, 17 · As an example, a classic result of Ritt shows that permutable polynomials are, up to a linear homeomorphism, either both powers of x, both iterates of the same polynomial, or both Chebychev polynomials We say f and g commute (with respect to composition) The property is called "commutativity"• Constant Multiple Rule g(x)=c·f(x)theng0(x)=c·f0(x) • Power Rule f(x)=x n thenf 0 (x)=nx n−1 • Sum and Difference Rule h(x)=f(x)±g(x)thenh 0 (x)=f 0 (x)±g 0 (x)
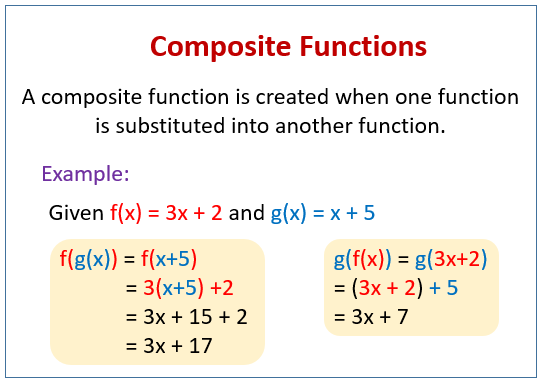



Composite Functions Video Lessons Examples And Solutions




Adidas X Ghosted 2 Fg Van Vaste Noppen
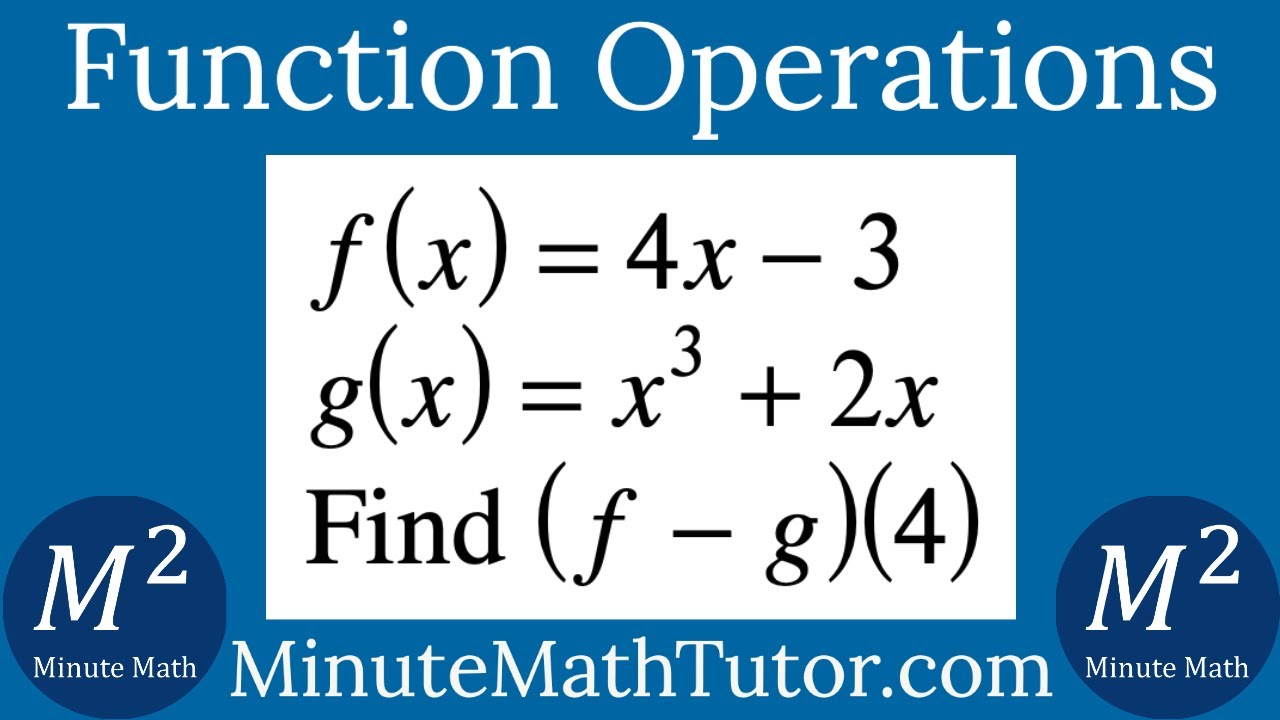



F X 4x 3 G X X 3 2x Find F G 4 Youtube




Bol Com Adidas X 19 3 Ll Fg Black Voetbalschoenen Maat 42




Adidas X Ghosted Fg Roze Adidas Officiele Shop




Adidas Performance X Ghosted 3 3 Fg Voetbalschoenen Zwart Grijs Ib125 Vergelijk Prijzen




Find F G F G Cf C R C 0 Fg 1f And 1g In Each Of The Following F X X 3 1 And G X X 1




Slate Digital Fg X Review Musicradar




Adidas X Ghosted 3 Ll Fg Van Vaste Noppen




Composite Functions Fg X And Gf X Gcse 9 1 New Topic Youtube




Adidas X 19 3 Fg Voetbalschoenen Heren Zwart Voetbal Geest




If F X 3x 1 And G X X 2 Find F G X Brainly Com




Example 17 Let F X Root X G X X Find F G Fg F G



People Highline Edu Awarnock Classnotes M141 2 7 Combining Functions Pdf




Adidas Heren Voetbalschoenen Fg X Ghosted 3 Fg Eg8193 Kopen Bij Voorwinden Nl




Having Trouble Finding G X When Given F X And Fg X Askmath




Adidas X 17 1 Fg Aero Green Unitiy Ink Damesschoenen Nl




Phantom Gt Elite Fg X Skepta Bloody Chrome Releasedatum Nike Snkrs Nl




8 If F X 3x 5 G X 6x 1 Then Find A F G X B F 9 2 C Fg 3 D F G X And Its Domain




Adidas X Ghosted 3 Fg Eh23 Intersport Theo Tol
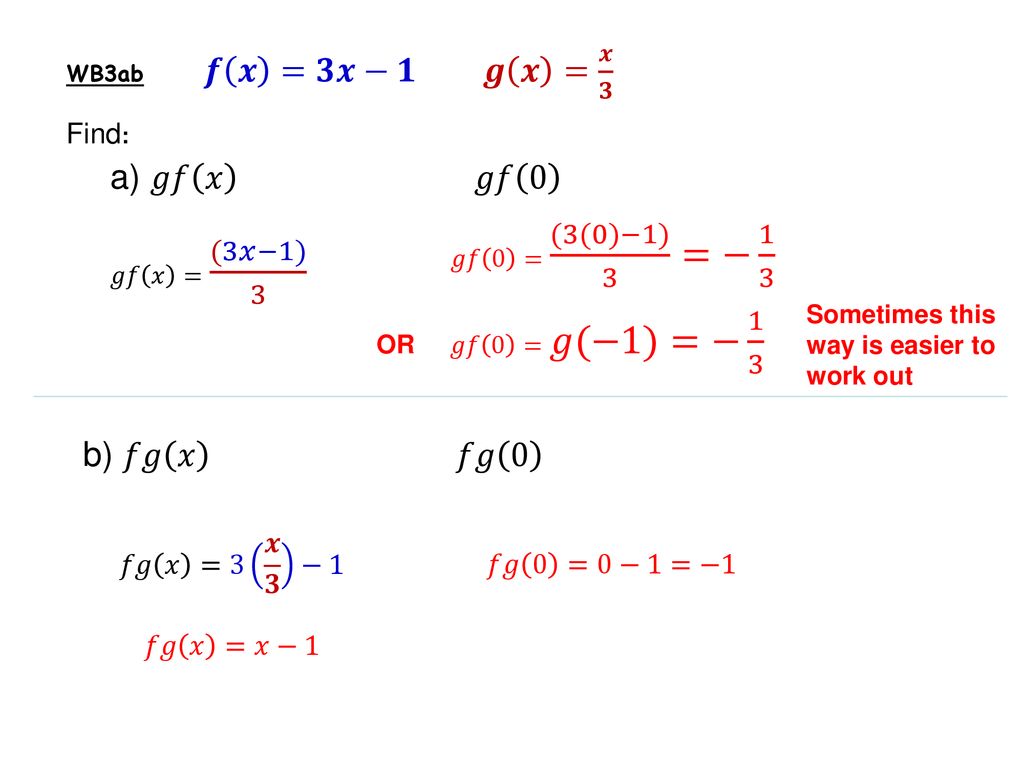



Functions Composite Ppt Download



Adidas X Ghosted 3 Ll Fg Voetbalschoenen Wit Zwart



Theorem For Limits Of Composite Functions Video Khan Academy
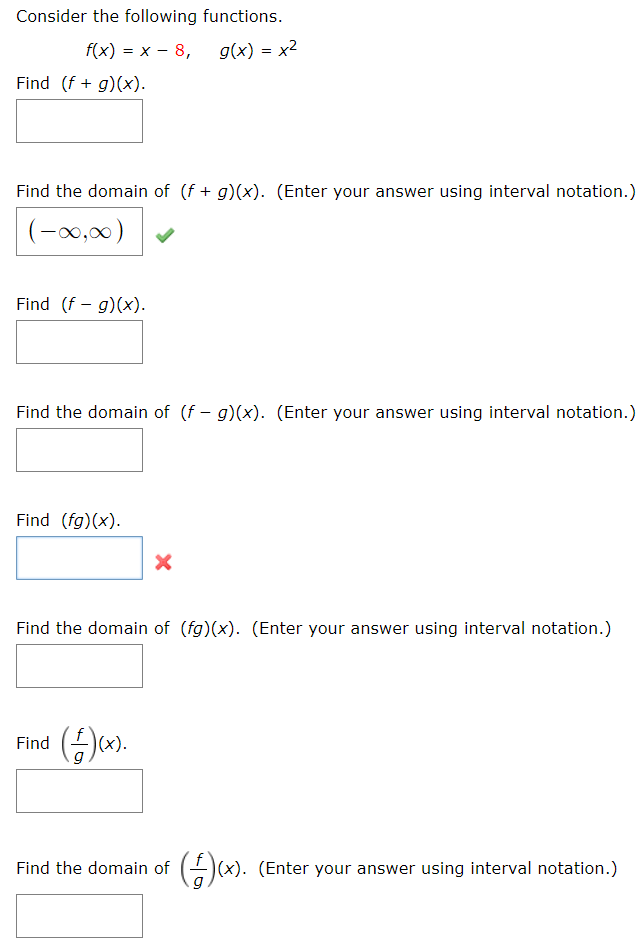



Consider The Following Functions F X X 8 G X X2 Chegg Com




Example 17 Let F X Root X G X X Find F G Fg F G




Adidas Jongens Voetbalschoenen Fg X Ghosted 3 Fg J Eg10 Kopen Bij Voorwinden Nl




Frank Dental D 0 014 Sg Fg




Bol Com Adidas X 17 3 Fg Heren Maat 39 1 3




Answered Consider The Following Functions F X Bartleby
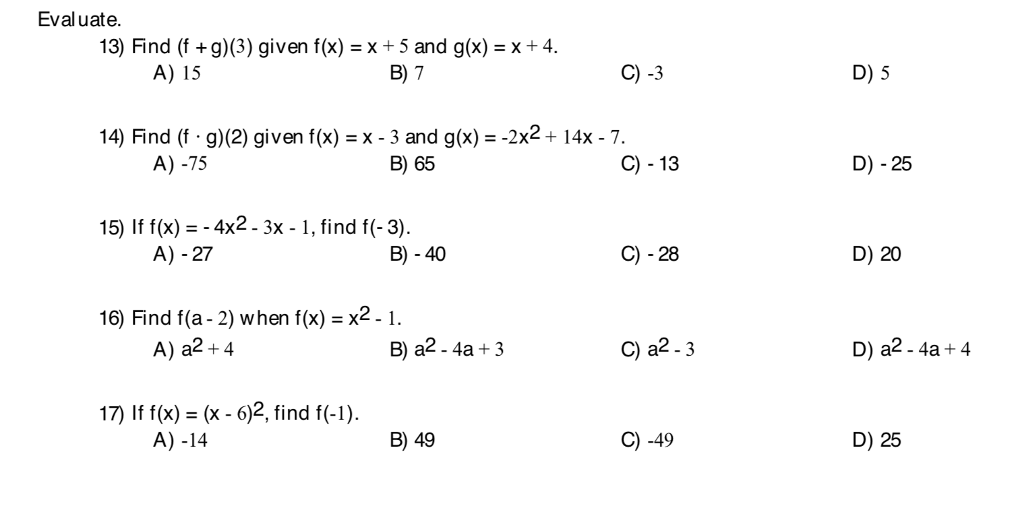



Evaluate 13 Find Fg 3 Given F X X 5 And G X X Chegg Com
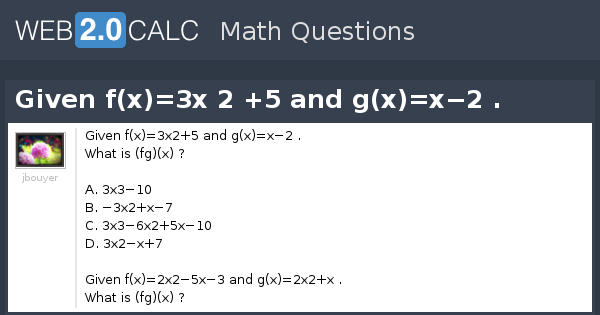



View Question Given F X 3x 2 5 And G X X 2




Adidas X Ghosted 2 Fg Zwart Sport Inn Zwolle




Frank Dental D 850 021 Sg Fg
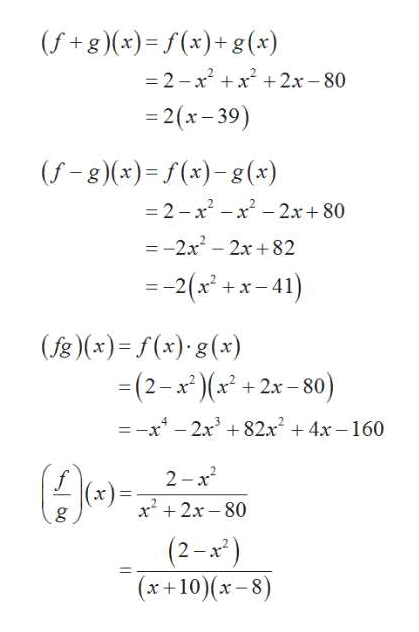



Answered For The Functions F X 2 X2 And G X X2 Bartleby



1




Adidas X Ghosted Fg Ag Superlative Geel Zwart Blauw Www Unisportstore Nl




Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 11 Chapter 3 Functions



1




Adidas X Ghosted Fg R Gol Com Football Boots Equipment




Adidas Heren Voetbalschoenen Fg X Ghosted 3 Fg Eh23 Kopen Bij Voorwinden Nl




Adidas X Ghosted Gras Voetbalschoenen Fg Kids Groen Paars




Bol Com Adidas X 19 3 Fg Junior Groen Oranje




Given The Graphs Of F X And G X Sketch The Graph Of F G X On The Same Grid Mathematics Stack Exchange




Adidas X Ghosted 3 Veterloos Fg Wit Sport Inn Zwolle




Find The Following F X 2x 3 G X 2 X F Chegg Com



Frank Dental D G368 0 G Fg




If F X 3x 2 2 And G X 2x 4 Find F G X Brainly Com




Adidas X 19 1 Fg Ag Locality Roze Www Unisportstore Nl
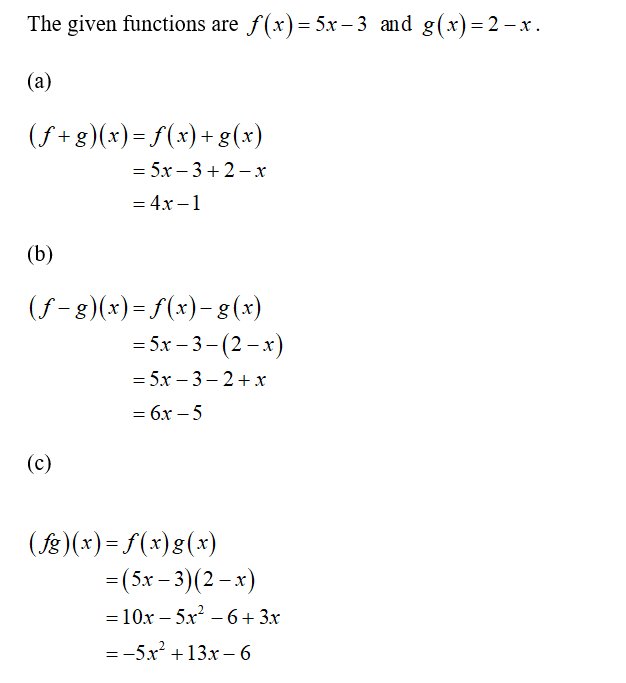



How To Find F G X




Composite Functions The Composite Function Fg Means Apply The Rule For G Then Apply The Rule For F So If F X X 2 And G X 3x 1 Then Fg 2 Ppt Download
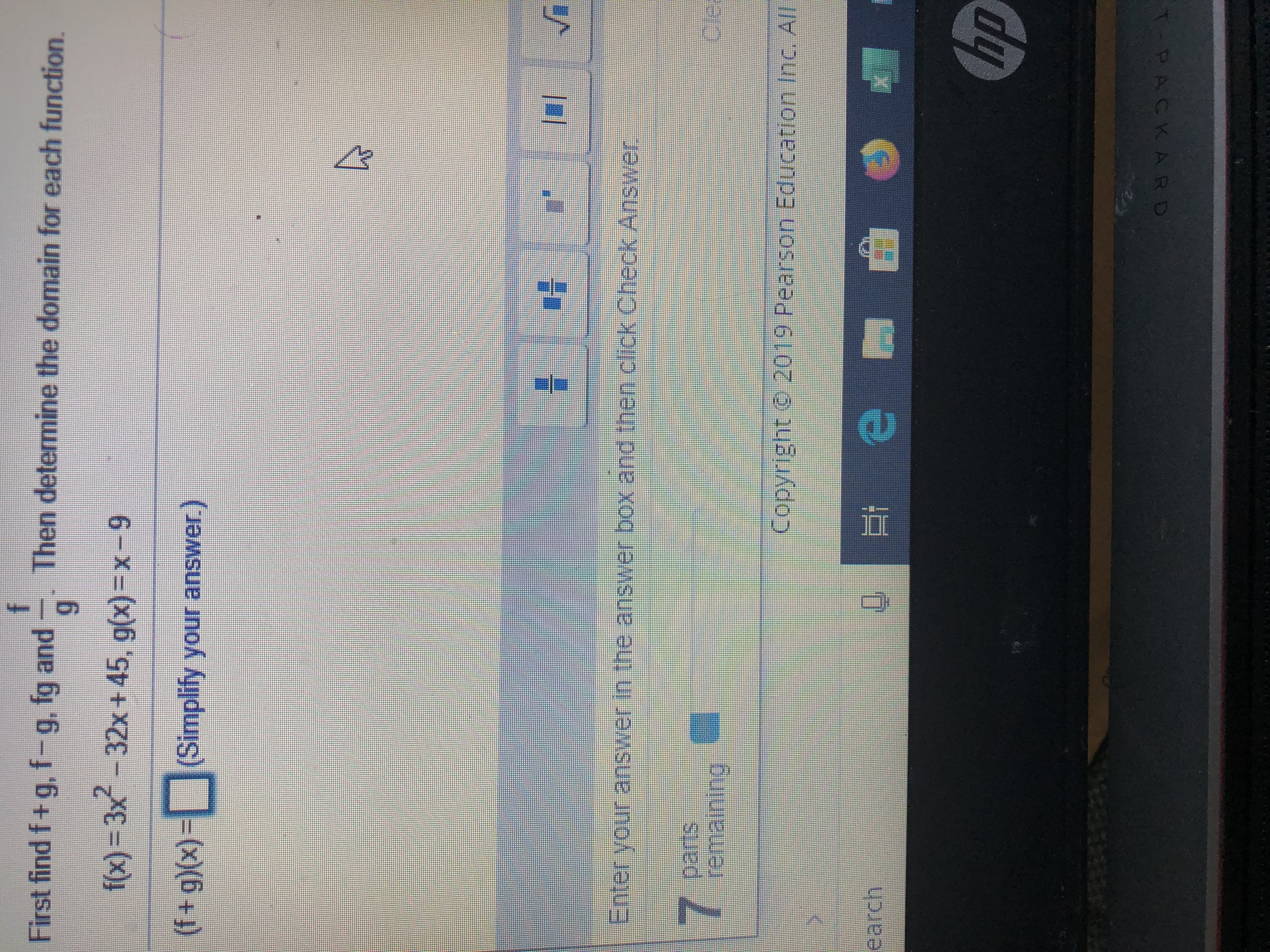



Answered F Then Determine The Domain For Each Bartleby
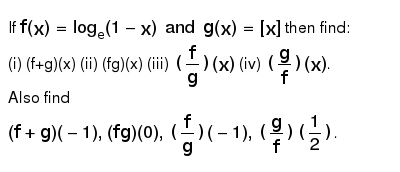



If F X Log E 1 X Andg X X Then Find I F G X Ii Fg




If F X X 2 And G X 2x Then Evaluate I F G 3




Let F X X 2and G X 2x 1be Two Real Functions Find




Adidas Voetbalschoenen Fg Heren X Ghosted 2 Fg Eh24 Kopen Bij Voorwinden Nl




Example 16 Let F X X2 And G X 2x 1 Find F G Fg F G




Adidas X Ghosted 3 Fg J Fw6934 Www Daka Nl




If F X 3x 1 And G X X 2 6 Find F G X Brainly Com
%20%205%20Verzinkt%20FG%20Wood%20connectors%20Per%201%20stuks%20FG01590010551405%205410439322218%20%20www.toolland.nl.png)



Koppelplaat Fg159 Fg162 Pgb Fg159 z Koppelplaat Zwaar 3 0 40 X 100 Mm Verzinkt 1 St




8 If F X 3x 5 G X 6x 1 Then Find A F G X B F 9 2 C Fg 3 D F G X And Its Domain



1




If F X X 2 And G X 2 X Find Solution Set Of Fog X Gof X




If F X 5 4 And G X 3 2 Find F G X Brainly Com




Adidas X Ghosted 2 Fg Wit Sport Inn Zwolle
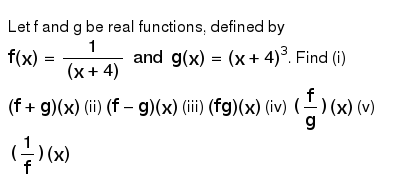



Let F And G Be Real Functions Defined By F X 1 X 4 Andg X
%20muliegaten%20merk-FG%20Verzinkt%201%20stuks%20FG02360011000405.%205410439360517%20www.toolland.nl-.png)



Versterkingshoek Fg236 Versterkingshoek 40 X 40 X 100 Mm 2 0 Muliegaten Merk Fg Verzinkt 1 Stuks
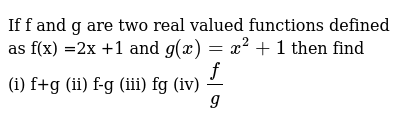



If F And G Are Two Real Valued Functions Defined As F X 2x 1 A




If F X 2x 2 1 And G X X 2 7 Find F G X Brainly Com



1
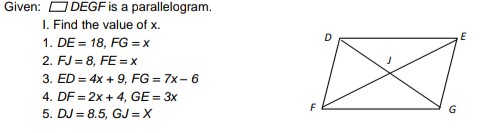



Answered Given Odegf Is A Parallelogram I Bartleby




Adidas X Ghosted 3 Ll Gras Voetbalschoenen Fg Zwart Grijs
_mapping_diagram.jpg)



Composite Functions Key Stage 4
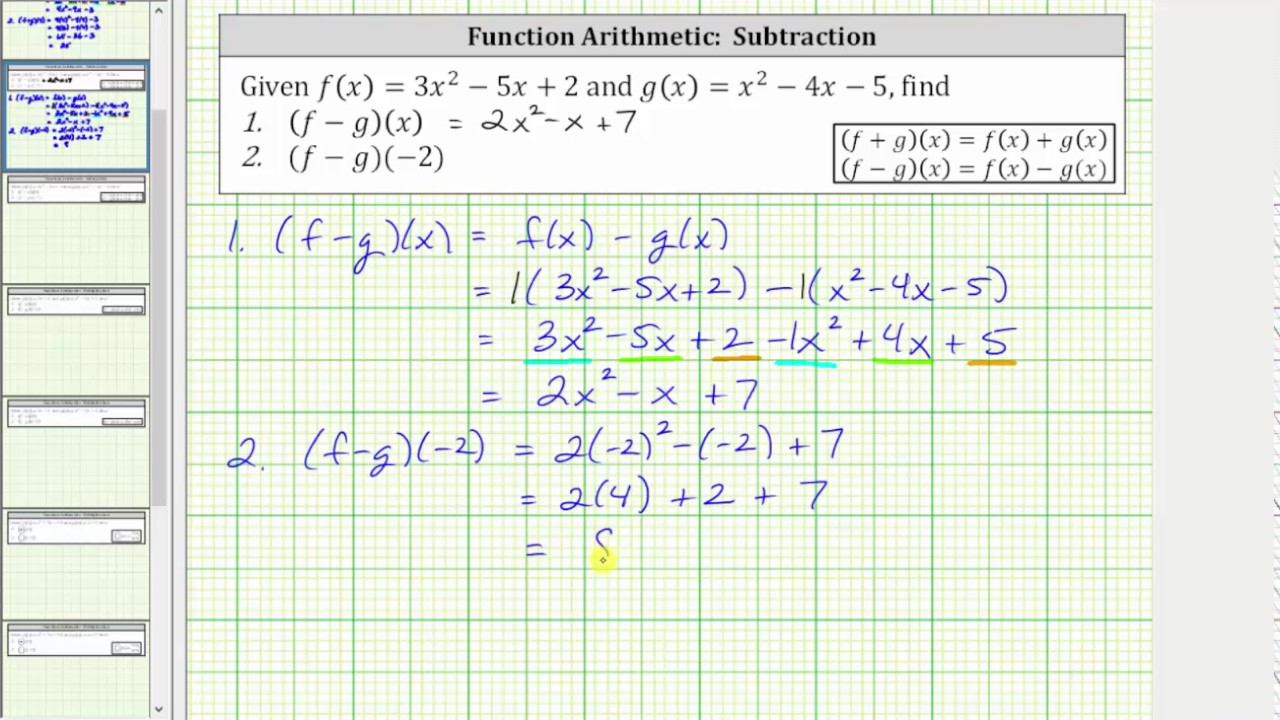



Function Arithmetic Difference F G X And F G 2 Quadratic Youtube
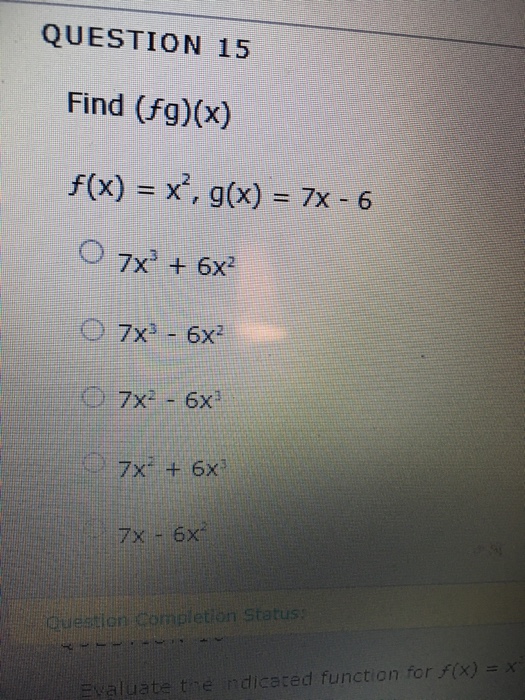



Find Fg X F X X 2 G X 7x 6 7x 3 6x 2 7x 3 6x 2 Chegg Com



Http Www Webassign Net Latex2pdf 1c4fdde6ea8f2bdb2f1ab9d4ac6143cb Pdf



Let The Function F R R Be Defined By F X X 3 X 2 X 1 Sin X And Let G R R Be An Arbitrary Function Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Adidas X 18 3 Fg J Kinderen Zwart Football Boots




Find F G X Youtube




Slate Digital Fg X




Adidas X Ghosted Fg Ag Inflight Wit Goud Zwart Www Unisportstore Nl


コメント
コメントを投稿